How to calculate Total Voltage and Total Capacity in Parallel Battery Connection?
How to wire batteries in parallel:
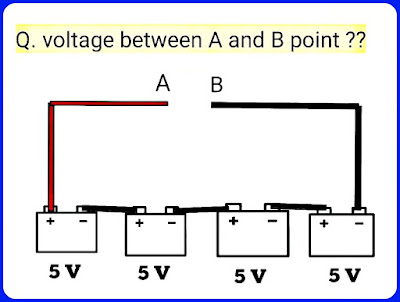
The parallel connection is the one of the type of battery connection. Parallel connections of batteries will increase your current rating, but the voltage will be stay the same.
Question:
 |
| How to Calculate Battery Total Voltage and Total Capacity in Parallel Battery Connection ? |
Solution:
Here we connected 4 batteries in parallel and each have 125Ah capacity and each have 12v battery voltage.
As per description "Parallel connections of batteries will increase your current rating, but the voltage will be stay the same."
Formula for Parallel Battery Connection
If each battery voltage is same,
Total Voltage = Same of Each battery voltage
Total Battery Capacity= No. Of Batteries × Capacity of each Battery
So as per Formula,
We have 4 batteries connected in parallel and each have same ratings that it has 125Ah battery capacity and each have 12v voltage.
So,
Total Voltage V = Same of Each battery voltage
= 12v
Total Capacity = No. Of Batteries × Capacity of each Battery
= 4 × 125
= 500 Ah
So our Final Answers are
- Total Voltage V = 12v
-
Total Capacity = 500Ah
To join batteries in parallel connection, we should use a jumper wire to connect both the positive terminals and other jumper wire to connect both the negative terminals of both batteries to each other.
Here connection should be done Negative to negative and positive to positive.
Here we can connect our load to one of the batteries, and it will drain all equally.
However, the best suitable method for keeping the batteries equalized is to connect to the positive at one end of connection of the battery pack, and the negative at the other end of connection to the pack.
It is also possible to connect batteries in series and parallel connection or configuration. By this way we can increase our voltage output and Amp/Hour rating.